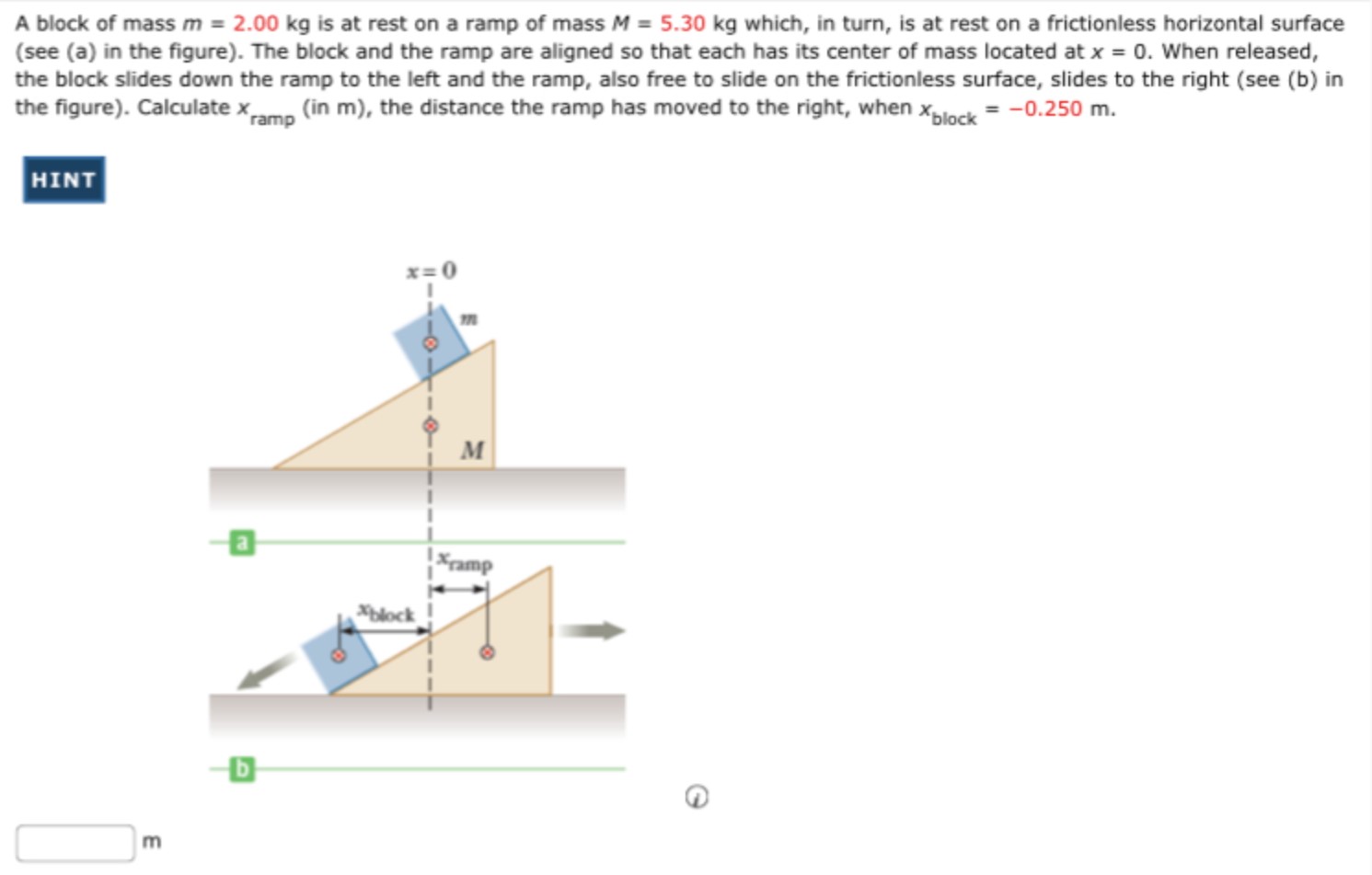
A block of mass m = 2.00 kg is at rest on a ramp of mass M = 5.30 kg which, in turn, is at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface (see (a) in the figure). The block and the ramp are aligned so that each has its center of mass located at x = 0. When released, the block slides down the ramp to the left and the ramp, also free to slide on the frictionless surface, slides to the right (see (b) in the figure). Calculate xramp (in m ), the distance the ramp has moved to the right, when xblock = −0.250 m. HINT m