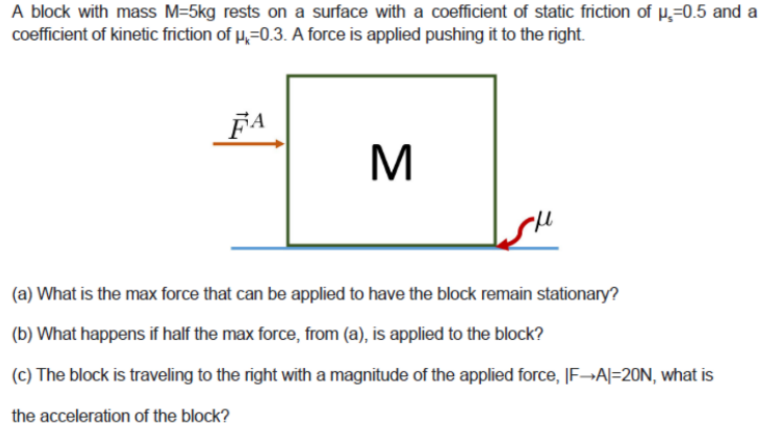
A block with mass M = 5 kg rests on a surface with a coefficient of static friction of μs = 0.5 and a coefficient of kinetic friction of μk = 0.3. A force is applied pushing it to the right. (a) What is the max force that can be applied to have the block remain stationary? (b) What happens if half the max force, from (a), is applied to the block? (c) The block is traveling to the right with a magnitude of the applied force, |F→A| = 20 N, what is the acceleration of the block?