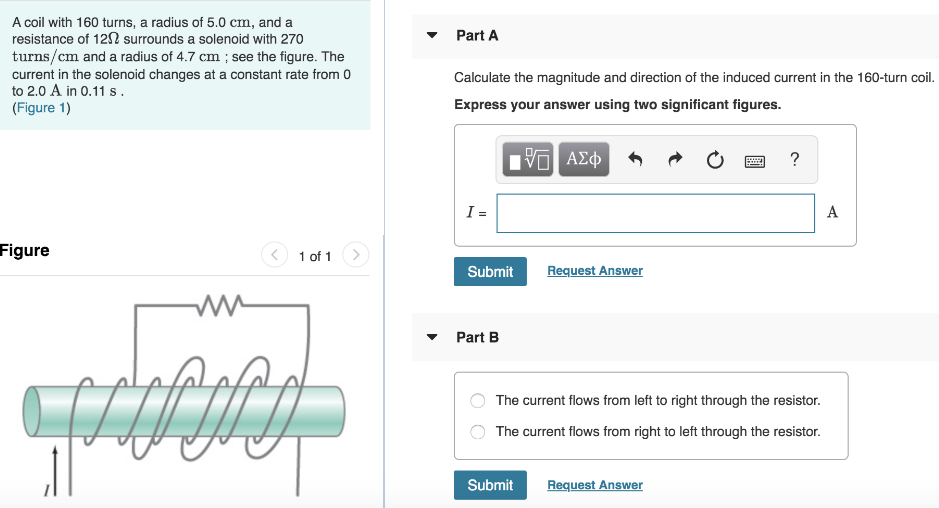
A coil with 160 turns, a radius of 5.0 cm, and a resistance of 12 Ω surrounds a solenoid with 270 turns/cm and a radius of 4.7 cm; see the figure. The current in the solenoid changes at a constant rate from 0 to 2.0 A in 0.11 s. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 Part A Calculate the magnitude and direction of the induced current in the 160-turn coil. Express your answer using two significant figures. Submit Request Answer Part B The current flows from left to right through the resistor. The current flows from right to left through the resistor. Submit Request Answer


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers