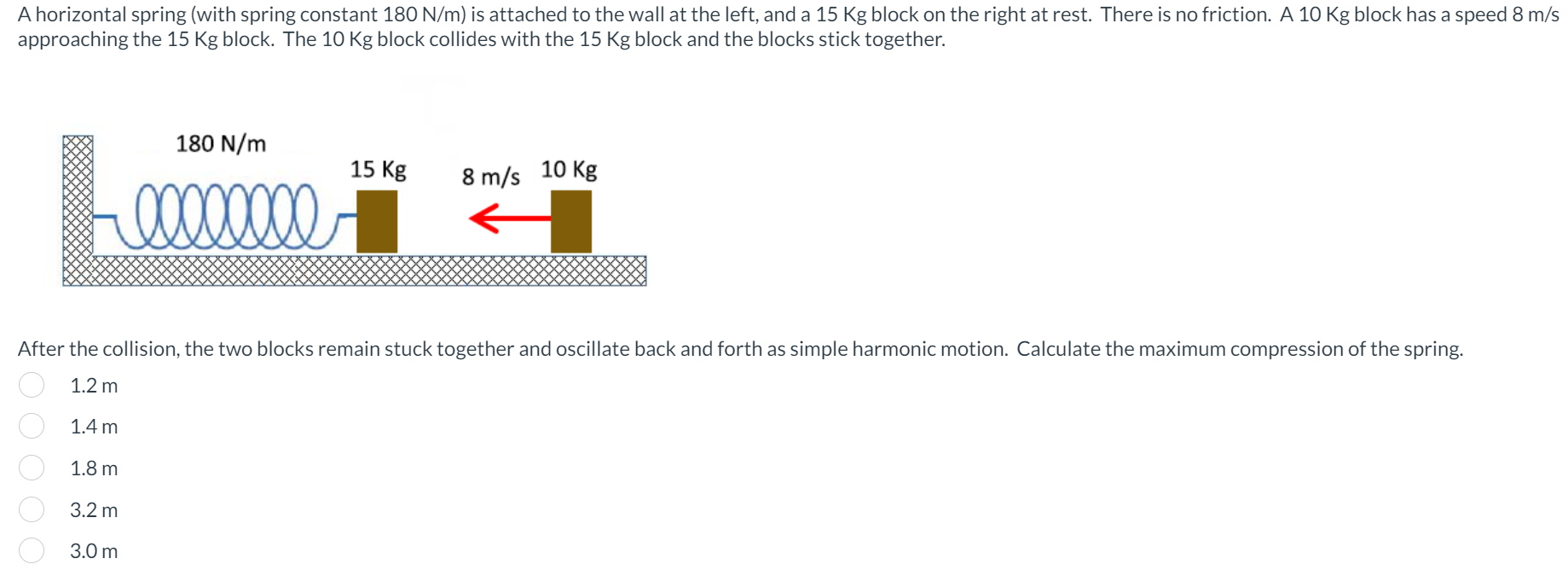
A horizontal spring (with spring constant 180 N/m) is attached to the wall at the left, and a 15 Kg block on the right at rest. There is no friction. A 10 Kg block has a speed 8 m/s approaching the 15 Kg block. The 10 Kg block collides with the 15 Kg block and the blocks stick together. After the collision, the two blocks remain stuck together and oscillate back and forth as simple harmonic motion. Calculate the maximum compression of the spring. 1.2 m 1.4 m 1.8 m 3.2 m 3.0 m