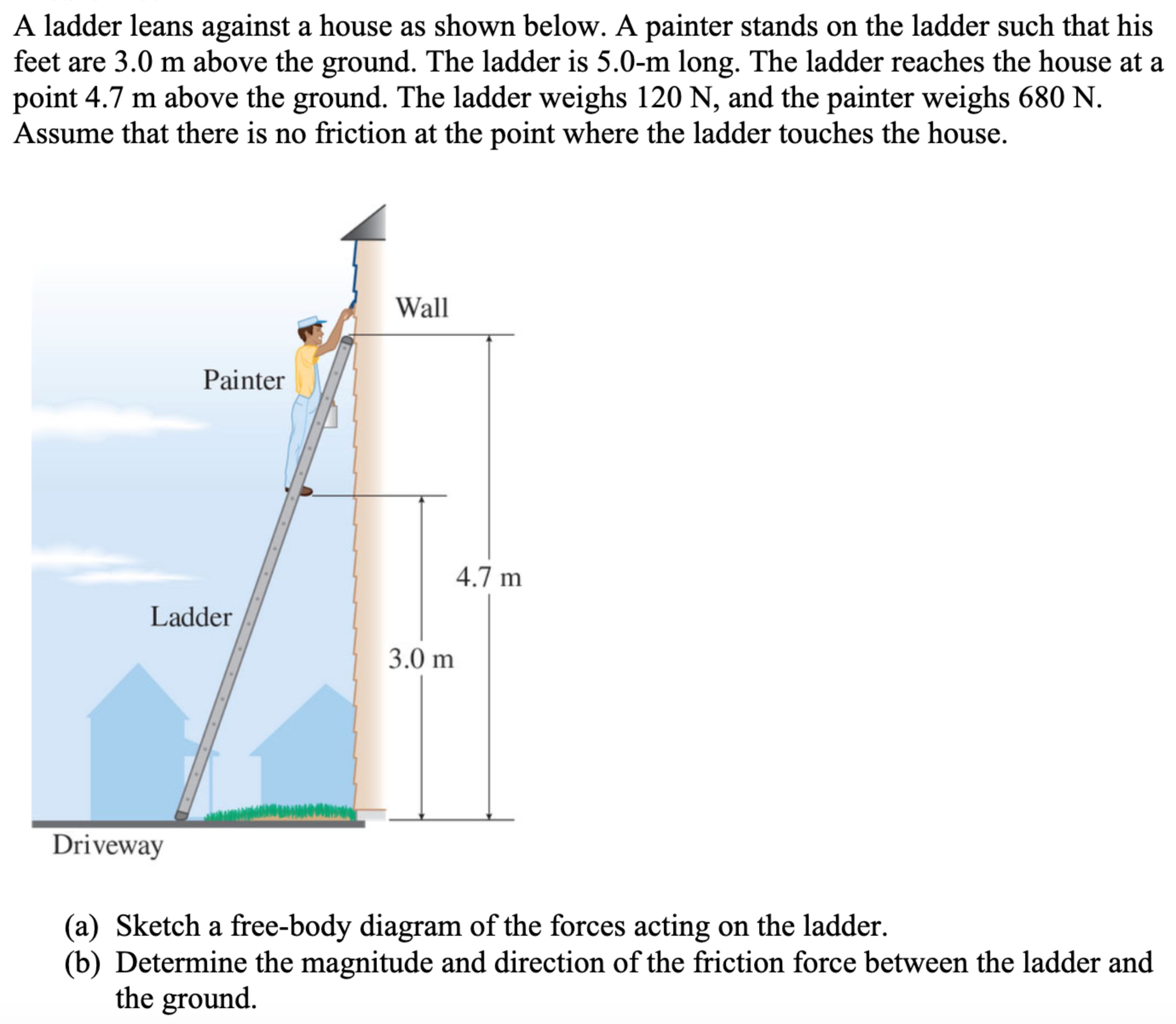
A ladder leans against a house as shown below. A painter stands on the ladder such that his feet are 3.0 m above the ground. The ladder is 5.0−m long. The ladder reaches the house at a point 4.7 m above the ground. The ladder weighs 120 N, and the painter weighs 680 N. Assume that there is no friction at the point where the ladder touches the house. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ladder. (b) Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force between the ladder and the ground.