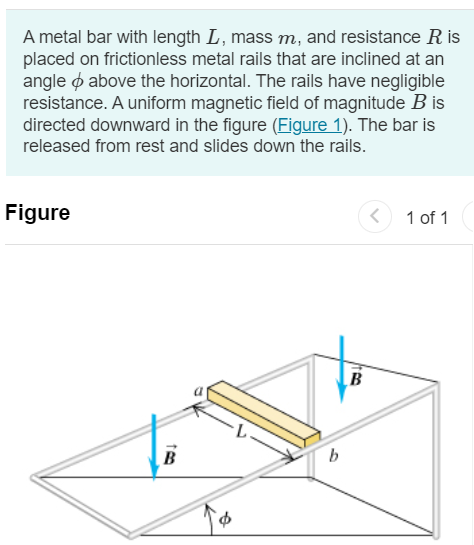
A metal bar with length L, mass m, and resistance R is placed on frictionless metal rails that are inclined at an angle ϕ above the horizontal. The rails have negligible resistance. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude B is directed downward in the figure (Figure 1). The bar is released from rest and slides down the rails. Figure 1 of 1 Part A Is the direction of the current induced in the bar from a to b or from b to a ? from a to b from b to a Submit Request Answer Part B What is the terminal speed of the bar? Express your answer in terms some or all of of the variables R, m, ϕ, L, B, and acceleration due to gravity g. vt = Submit Request Answer Part C What is the induced current in the bar when the terminal speed has been reached? Express your answer in terms some or all of of the variables R, m, ϕ, L, B, and acceleration due to gravity g. Submit Request Answer Part D After the terminal speed has been reached, at what rate is electrical energy being converted to thermal energy in the resistance of the bar? Express your answer in terms some or all of of the variables R, m, ϕ, L, B, and acceleration due to gravity g. Part E After the terminal speed has been reached, at what rate is work being done on the bar by gravity? Express your answer in terms some or all of of the variables R, m, ϕ, L, B, and acceleration due to gravity g. Submit Request Answer