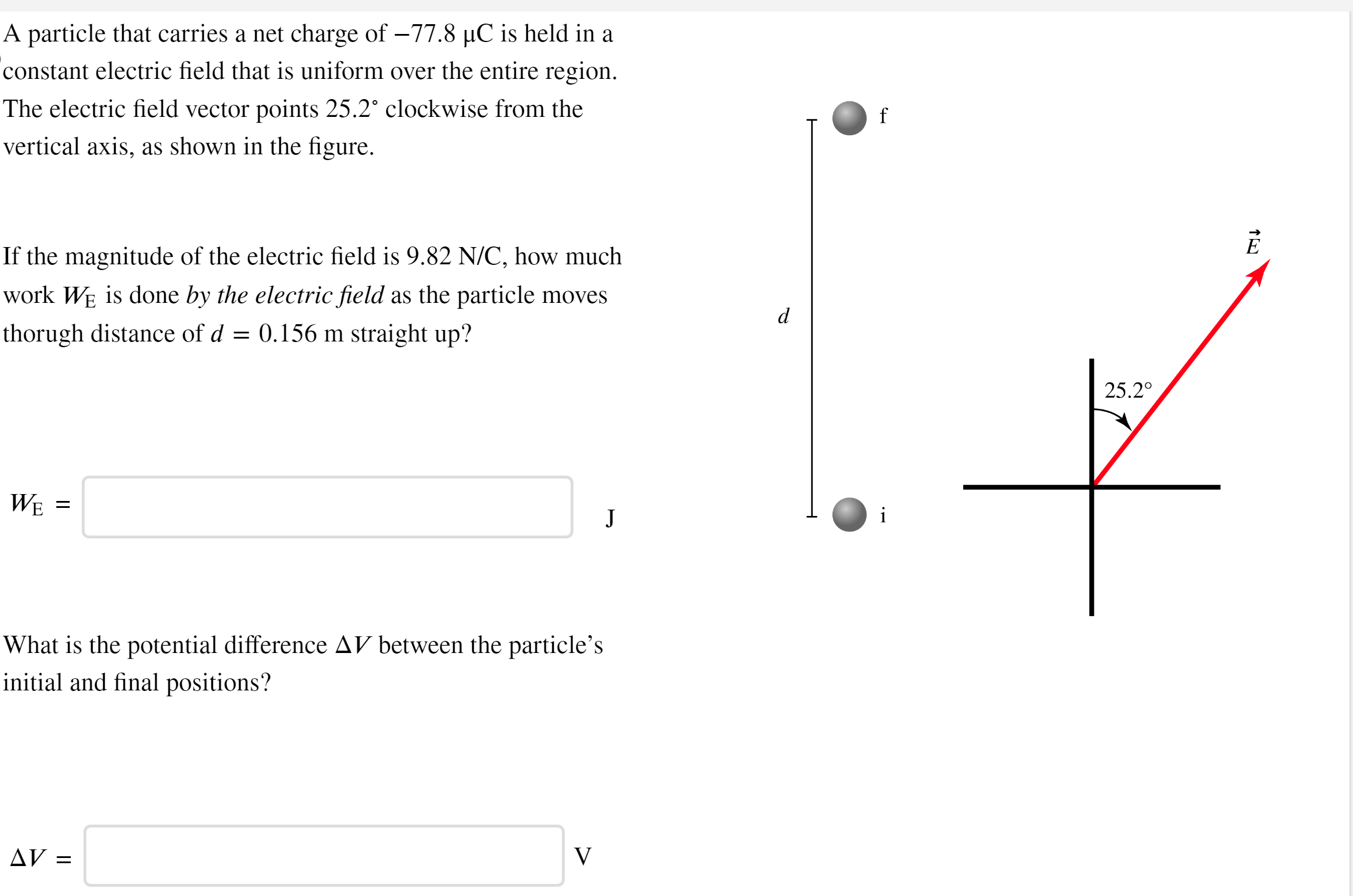
A particle that carries a net charge of −77.8 μC is held in a constant electric field that is uniform over the entire region. The electric field vector points 25.2∘ clockwise from the vertical axis, as shown in the figure. If the magnitude of the electric field is 9.82 N/C, how much work WE is done by the electric field as the particle moves thorugh distance of d = 0.156 m straight up? WE = J What is the potential difference ΔV between the particle's initial and final positions? ΔV = V