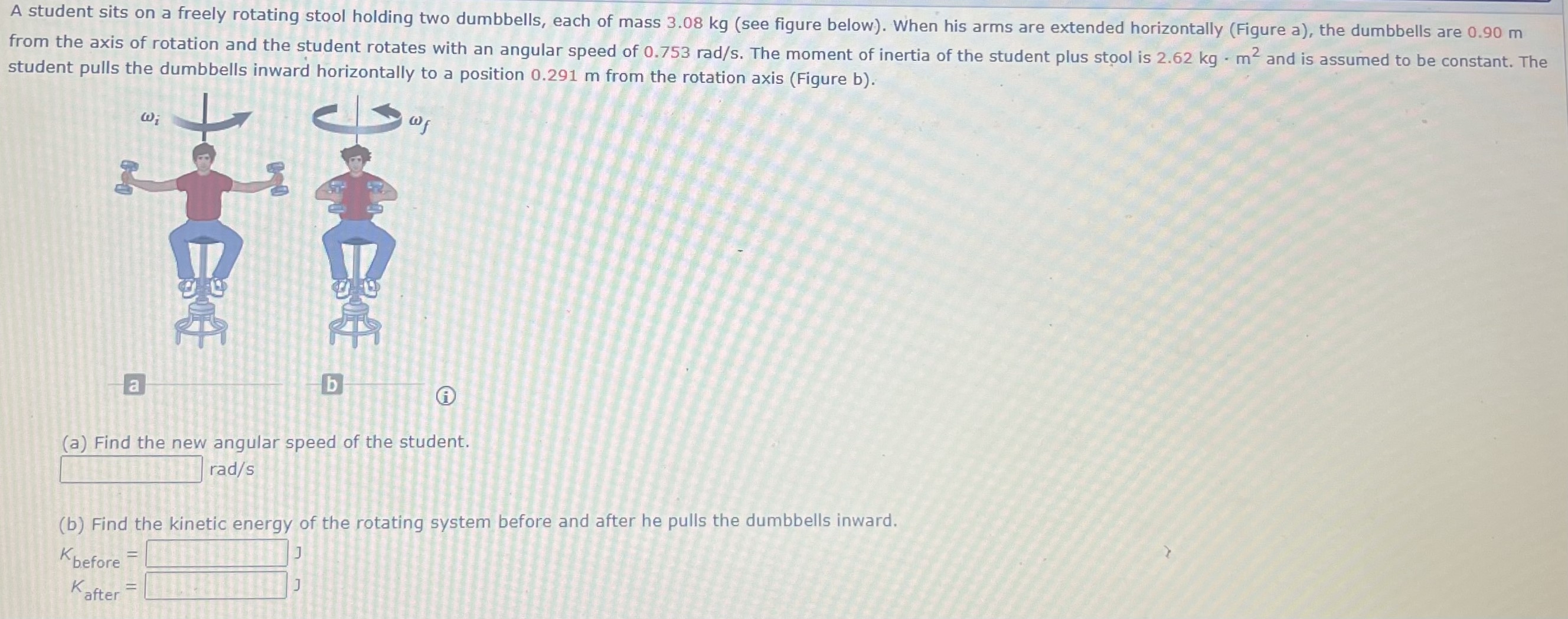
A student sits on a freely rotating stool holding two dumbbells, each of mass 3.08 kg (see figure below). When his arms are extended horizontally (Figure a), the dumbbells are 0.90 m from the axis of rotation and the student rotates with an angular speed of 0.753 rad/s. The moment of inertia of the student plus stool is 2.62 kg⋅m2 and is assumed to be constant. The student pulls the dumbbells inward horizontally to a position 0.291 m from the rotation axis (Figure b). a b (a) Find the new angular speed of the student. rad/s (b) Find the kinetic energy of the rotating system before and after he pulls the dumbbells inward. Kbefore = J Kafter = J