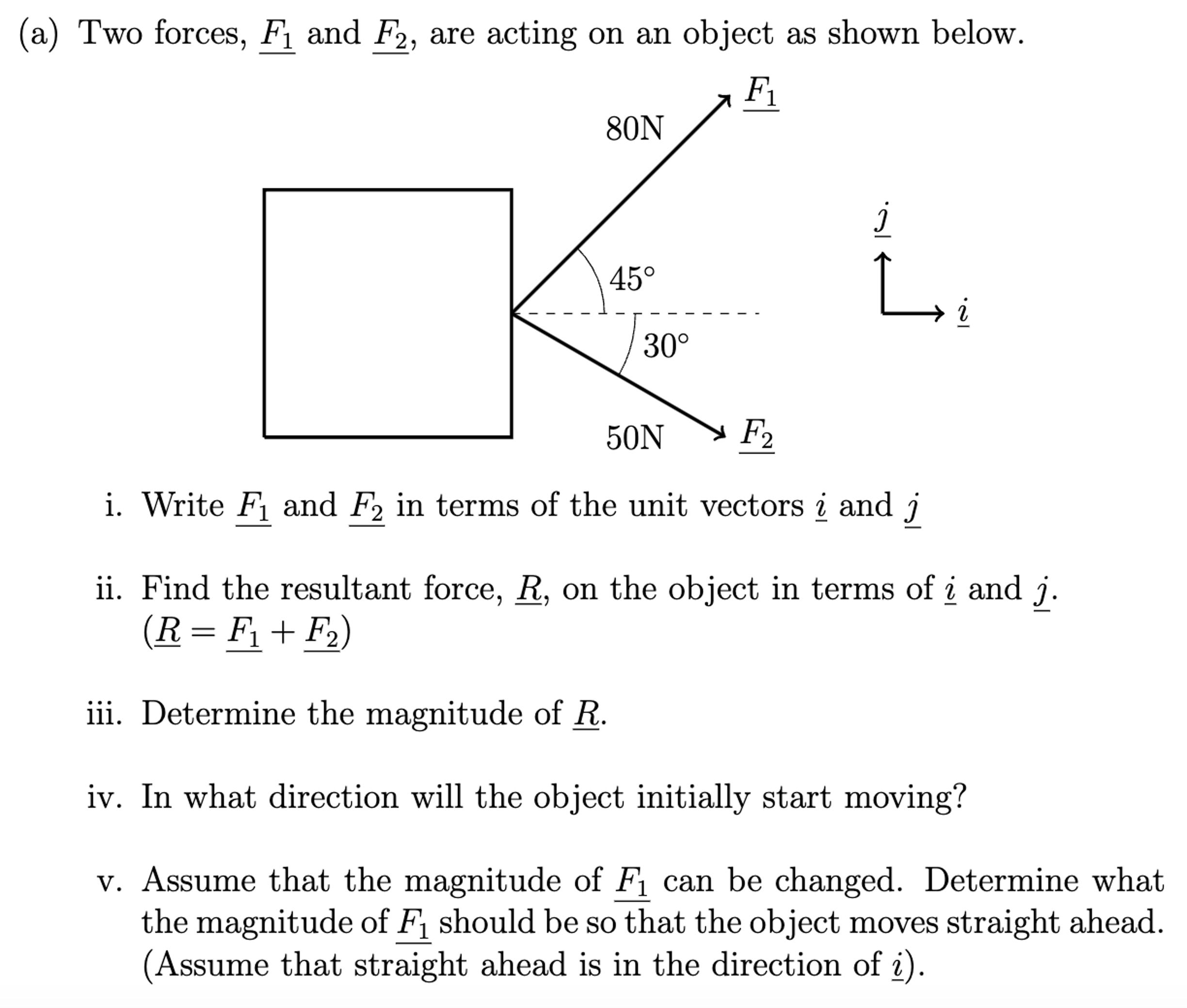
(a) Two forces, F1 and F2, are acting on an object as shown below. i. Write F1 and F2 in terms of the unit vectors i and j ii. Find the resultant force, R_, on the object in terms of i and j. (R = F1 + F2) iii. Determine the magnitude of R. iv. In what direction will the object initially start moving? v. Assume that the magnitude of F1 can be changed. Determine what the magnitude of F1 should be so that the object moves straight ahead. (Assume that straight ahead is in the direction of i).