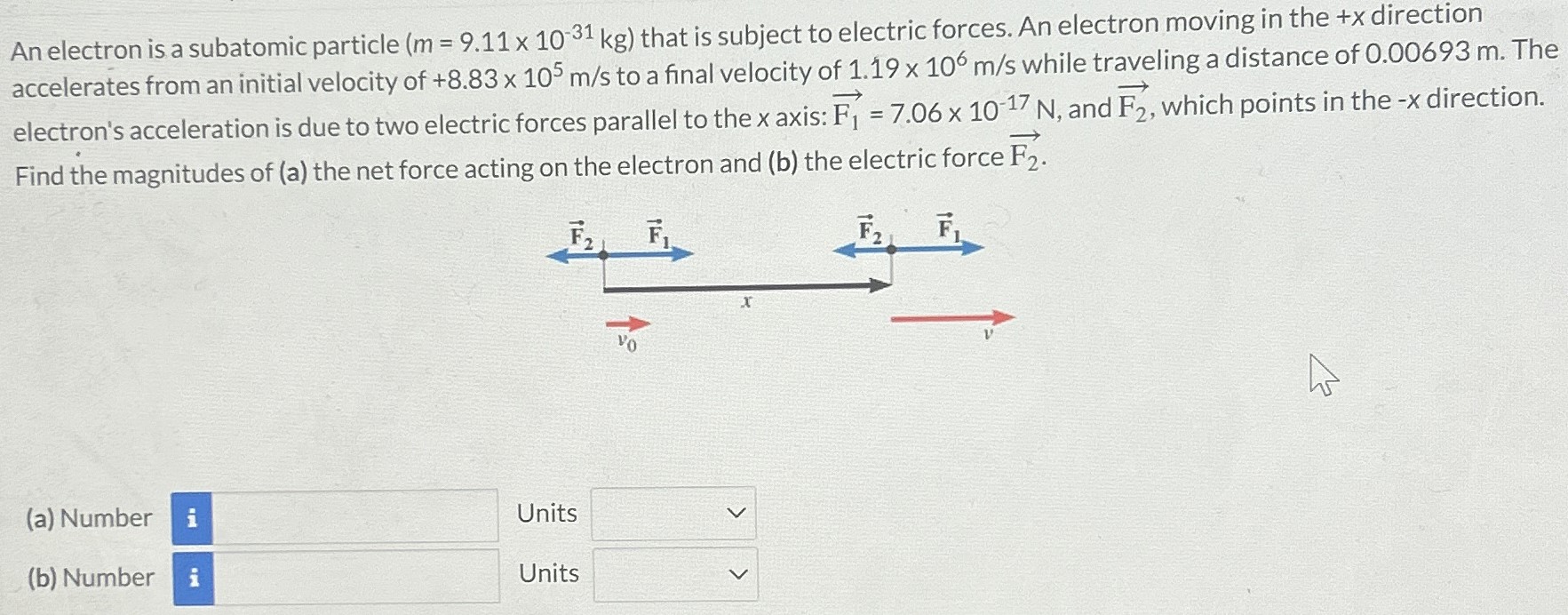
An electron is a subatomic particle (m = 9.11×10−31 kg) that is subject to electric forces. An electron moving in the +x direction accelerates from an initial velocity of +8.83×105 m/s to a final velocity of 1.19×106 m/s while traveling a distance of 0.00693 m. The electron's acceleration is due to two electric forces parallel to the x axis: F1→ = 7.06×10−17 N, and F2→, which points in the −x direction. Find the magnitudes of (a) the net force acting on the electron and (b) the electric force F2→. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units