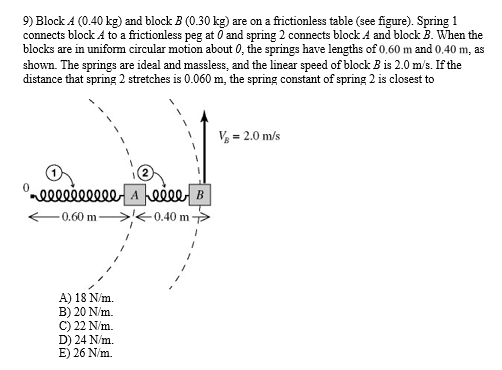
Block A (0.40 kg) and block B (0.30 kg) are on a frictionless table (see figure). Spring 1 connects block A to a frictionless peg at O and spring 2 connects block A and block B. When the blocks are in uniform circular motion about 0, the springs have lengths of 0.60 m and 0.40 m, as shown. The springs are ideal and massless, and the linear speed of block B is 2.0 m/s. If the distance that spring 2 stretches is 0.060 m, the spring constant of spring 2 is closest to A) 18 N/m. B) 20 N/m. C) 22 N/m. D) 24 N/m. E) 26 N/m.