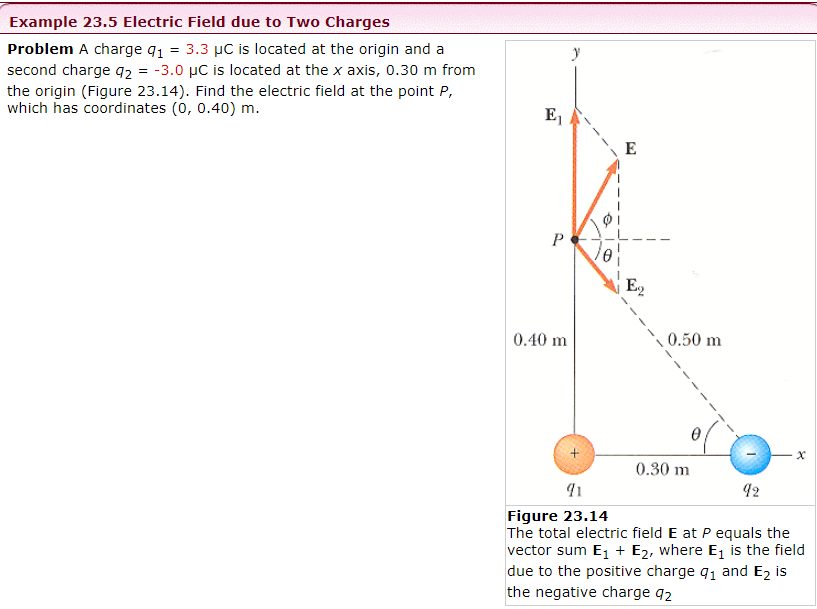
Example 23.5 Electric Field due to Two Charges Problem A charge q1 = 3.3 μC is located at the origin and a second charge q2 = −3.0 μC is located at the x axis, 0.30 m from the origin (Figure 23.14). Find the electric field at the point P, which has coordinates (0, 0.40)m. Figure 23.14 The total electric field E at P equals the vector sum E1 + E2, where E1 is the field due to the positive charge q1 and E2 is the negative charge q2