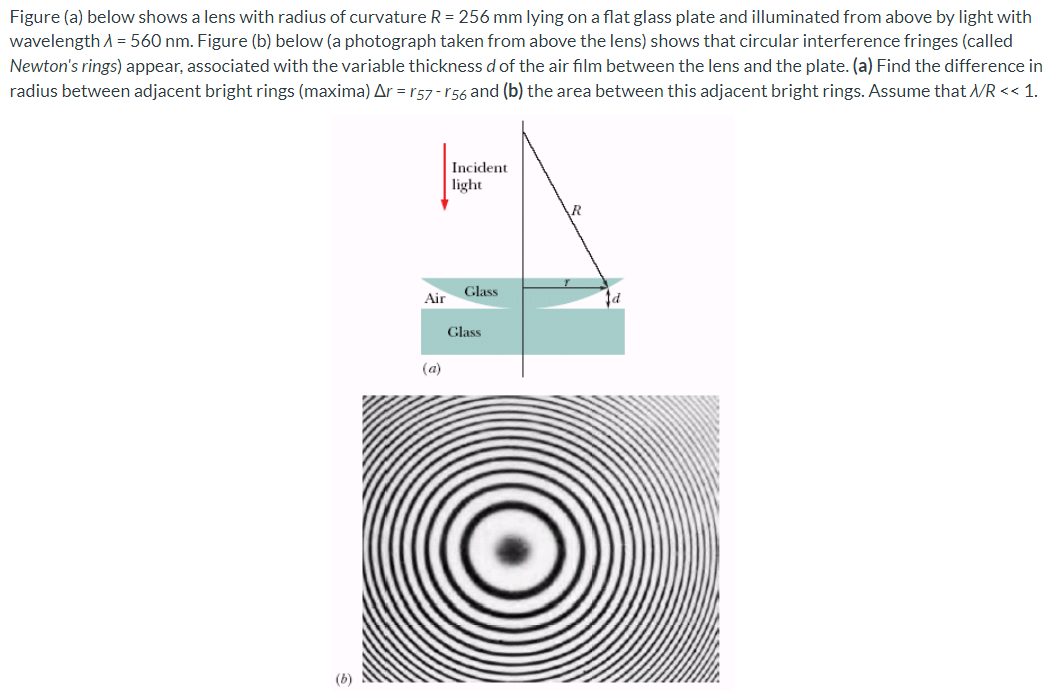
Figure (a) below shows a lens with radius of curvature R = 256 mm lying on a flat glass plate and illuminated from above by light with wavelength λ = 560 nm. Figure (b) below (a photograph taken from above the lens) shows that circular interference fringes (called Newton's rings) appear, associated with the variable thickness d of the air film between the lens and the plate. (a) Find the difference in radius between adjacent bright rings (maxima) Δr = r57 − r56 and (b) the area between this adjacent bright rings. Assume that λ/R < < 1. (a) (b)