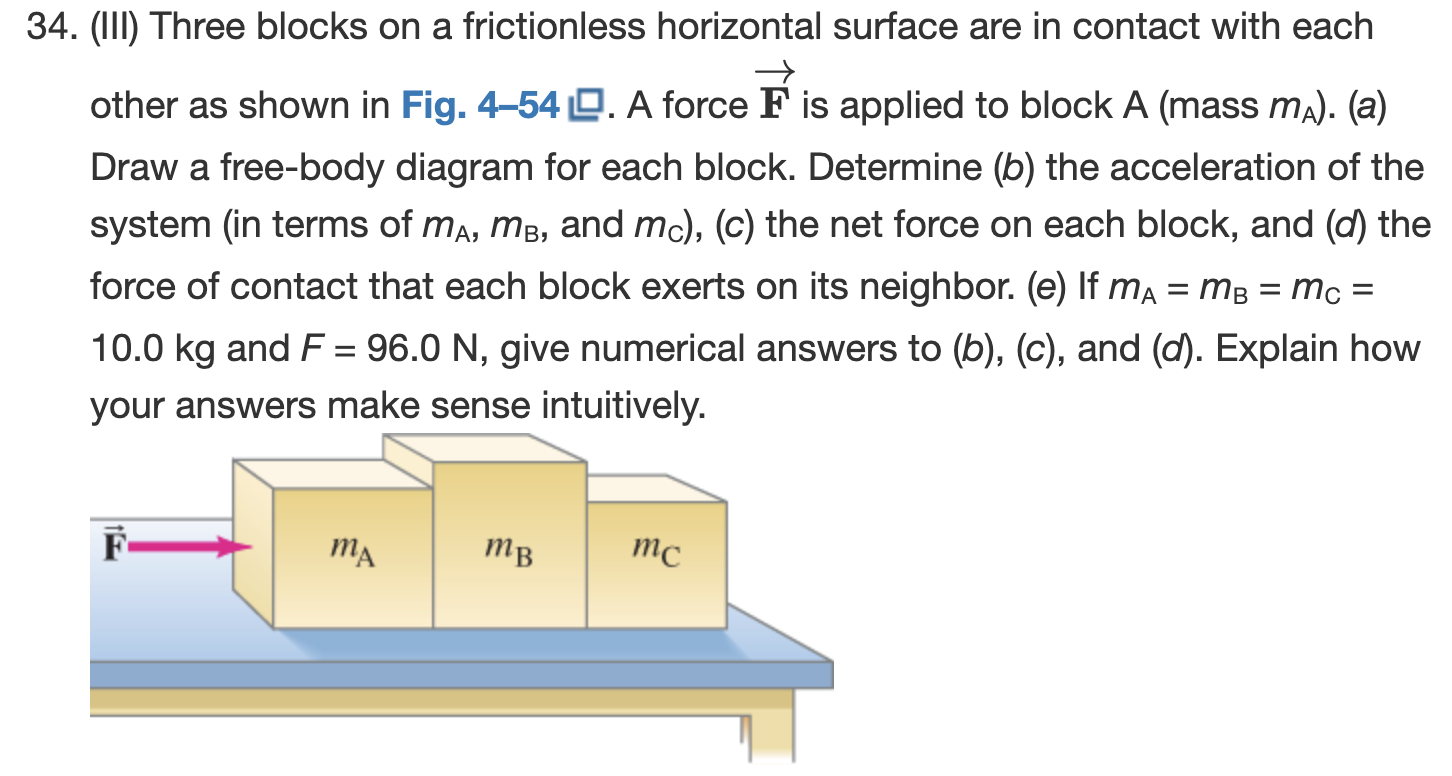
(III) Three blocks on a frictionless horizontal surface are in contact with each other as shown in Fig. 4-54. A force F→ is applied to block A (mass mA). (a) Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Determine (b) the acceleration of the system (in terms of mA, mB, and mC), (c) the net force on each block, and (d) the force of contact that each block exerts on its neighbor. (e) If mA = mB = mC = 10.0 kg and F = 96.0 N, give numerical answers to (b), (c), and (d). Explain how your answers make sense intuitively.