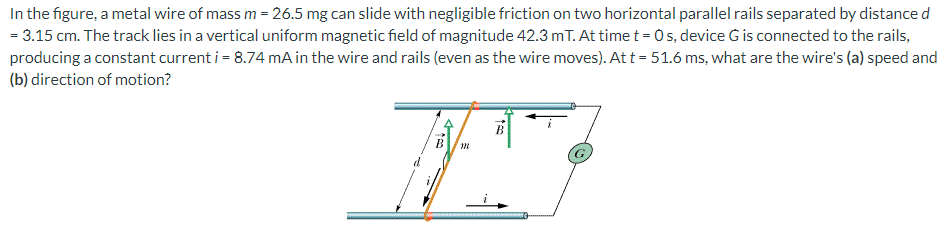
In the figure, a metal wire of mass m = 26.5 mg can slide with negligible friction on two horizontal parallel rails separated by distance d = 3.15 cm. The track lies in a vertical uniform magnetic field of magnitude 42.3 mT. At time t = 0 s, device G is connected to the rails, producing a constant current i = 8.74 mA in the wire and rails (even as the wire moves). At t = 51.6 ms, what are the wire's (a) speed and (b) direction of motion?