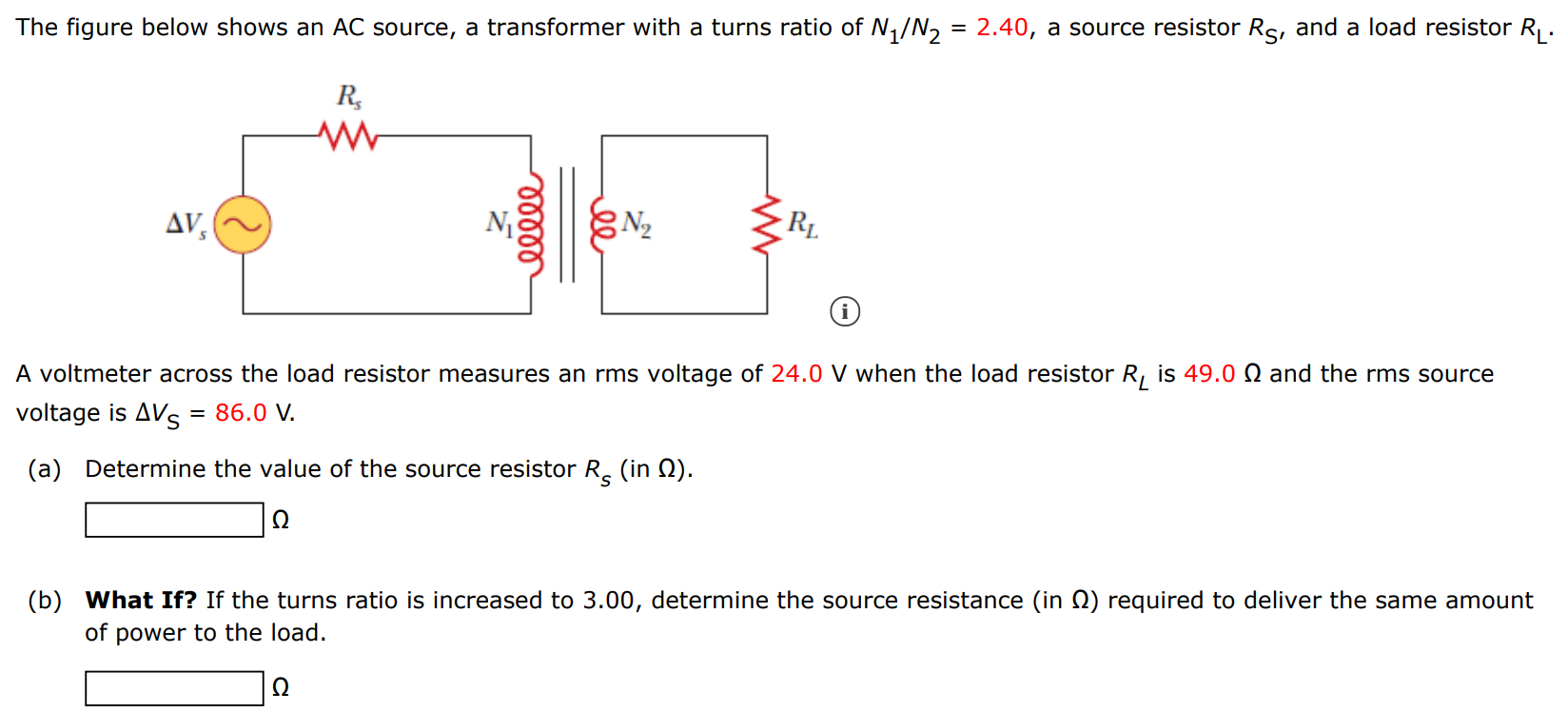
The figure below shows an AC source, a transformer with a turns ratio of N1/N2 = 2.40, a source resistor RS, and a load resistor RL. A voltmeter across the load resistor measures an rms voltage of 24.0 V when the load resistor RL is 49.0 Ω and the rms source voltage is ΔVS = 86.0 V. (a) Determine the value of the source resistor RS (in Ω). Ω (b) What If? If the turns ratio is increased to 3.00, determine the source resistance (in Ω) required to deliver the same amount of power to the load. Ω