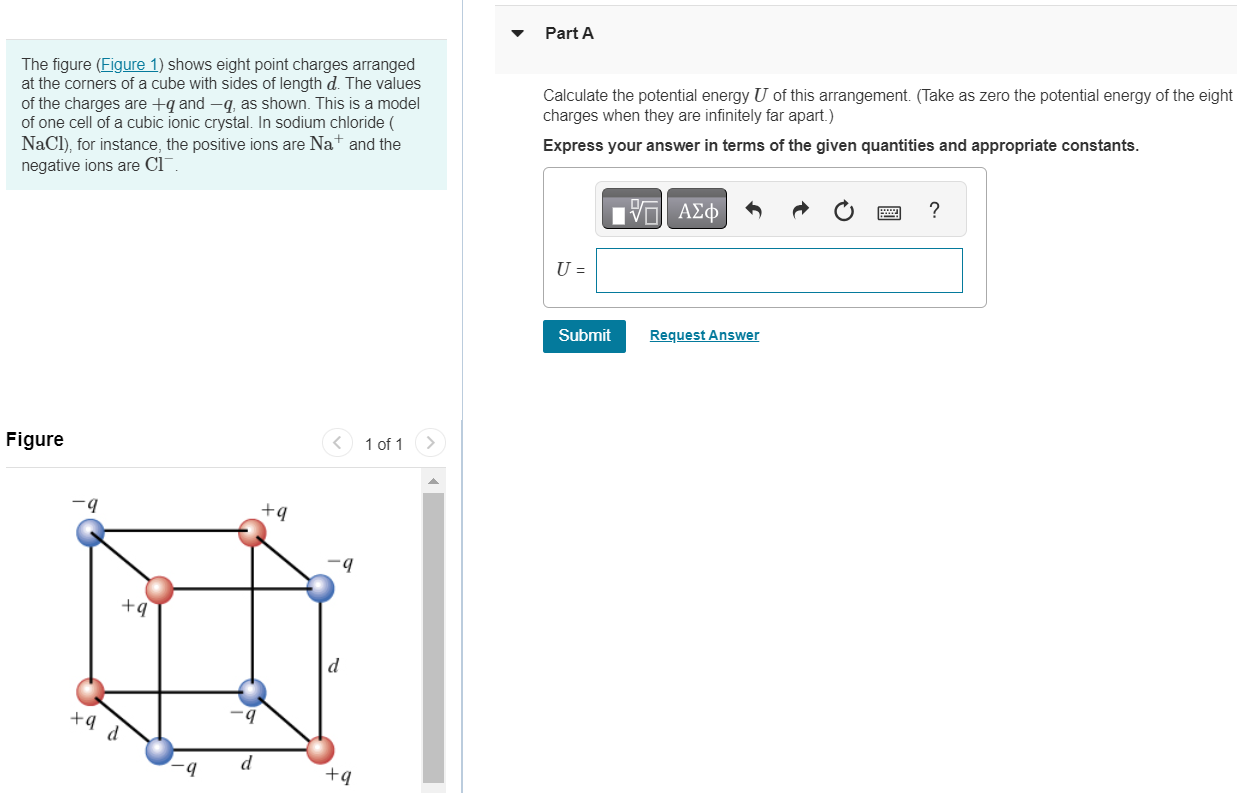
The figure (Figure 1) shows eight point charges arranged at the corners of a cube with sides of length d. The values of the charges are +q and −q, as shown. This is a model of one cell of a cubic ionic crystal. In sodium chloride ( NaCl), for instance, the positive ions are Na+ and the negative ions are Cl−. Figure 1 of 1 Part A Calculate the potential energy U of this arrangement. (Take as zero the potential energy of the eight charges when they are infinitely far apart. ) Express your answer in terms of the given quantities and appropriate constants. U = Submit Request Answer