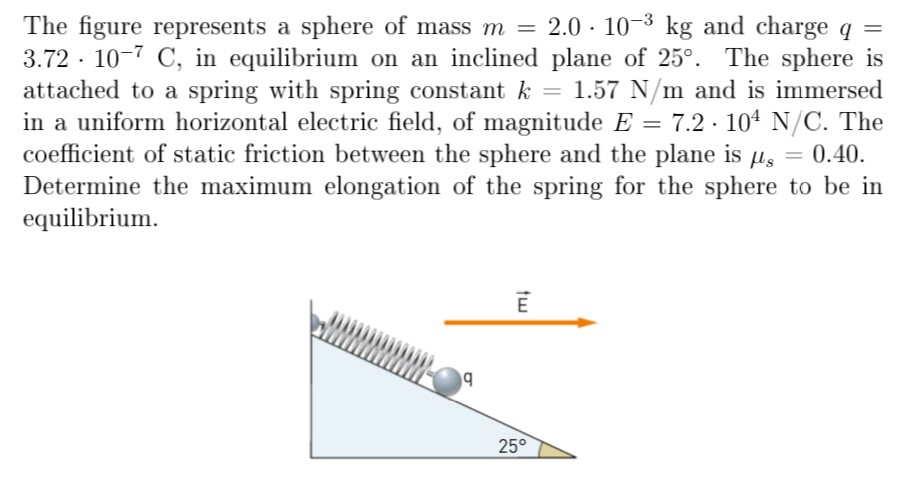
The figure represents a sphere of mass m = 2.0⋅10−3 kg and charge q = 3.72⋅10−7 C, in equilibrium on an inclined plane of 25∘. The sphere is attached to a spring with spring constant k = 1.57 N/m and is immersed in a uniform horizontal electric field, of magnitude E = 7.2⋅104 N/C. The coefficient of static friction between the sphere and the plane is μs = 0.40. Determine the maximum elongation of the spring for the sphere to be in equilibrium.