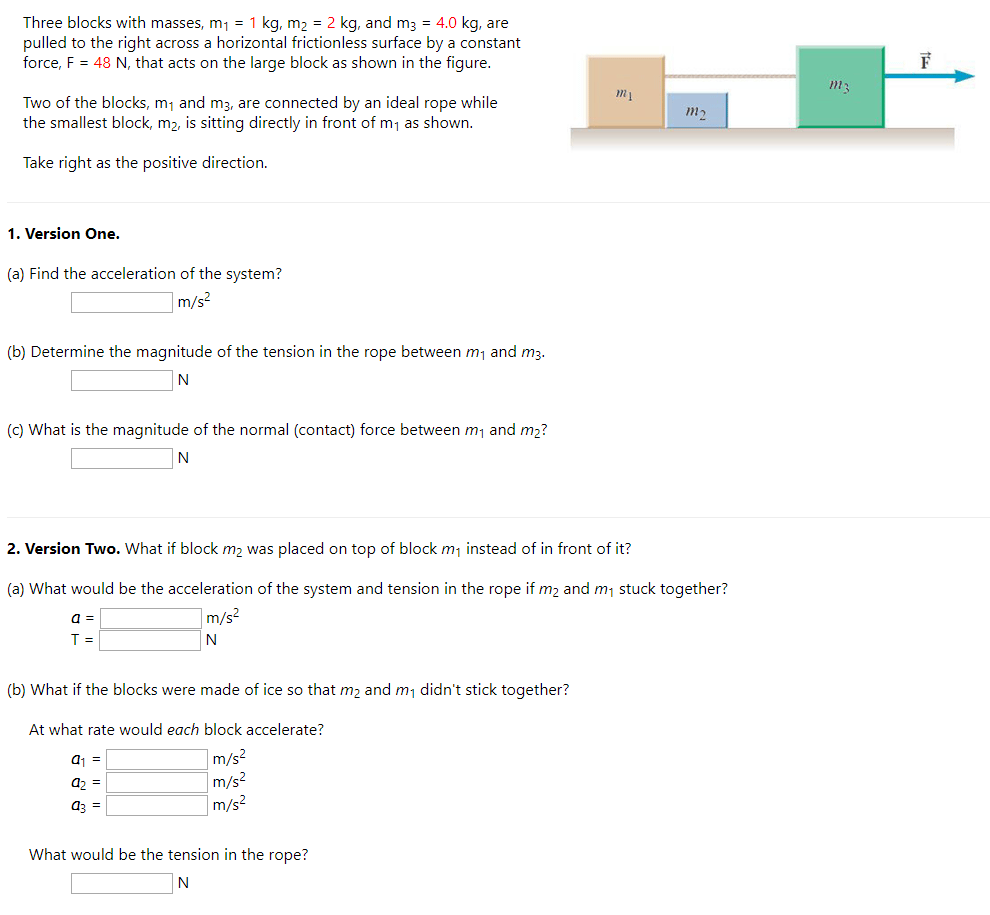
Three blocks with masses, m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg, and m3 = 4.0 kg, are pulled to the right across a horizontal frictionless surface by a constant force, F = 48 N, that acts on the large block as shown in the figure. Two of the blocks, m1 and m3, are connected by an ideal rope while the smallest block, m2, is sitting directly in front of m1 as shown. Take right as the positive direction. Version One. (a) Find the acceleration of the system? m/s2 (b) Determine the magnitude of the tension in the rope between m1 and m3. N (c) What is the magnitude of the normal (contact) force between m1 and m2 ? N Version Two. What if block m2 was placed on top of block m1 instead of in front of it? (a) What would be the acceleration of the system and tension in the rope if m2 and m1 stuck together? a = m/s2 T = N (b) What if the blocks were made of ice so that m2 and m1 didn't stick together? At what rate would each block accelerate? a1 = m/s2 a2 = m/s2 a3 = m/s2 a3 = What would be the tension in the rope?