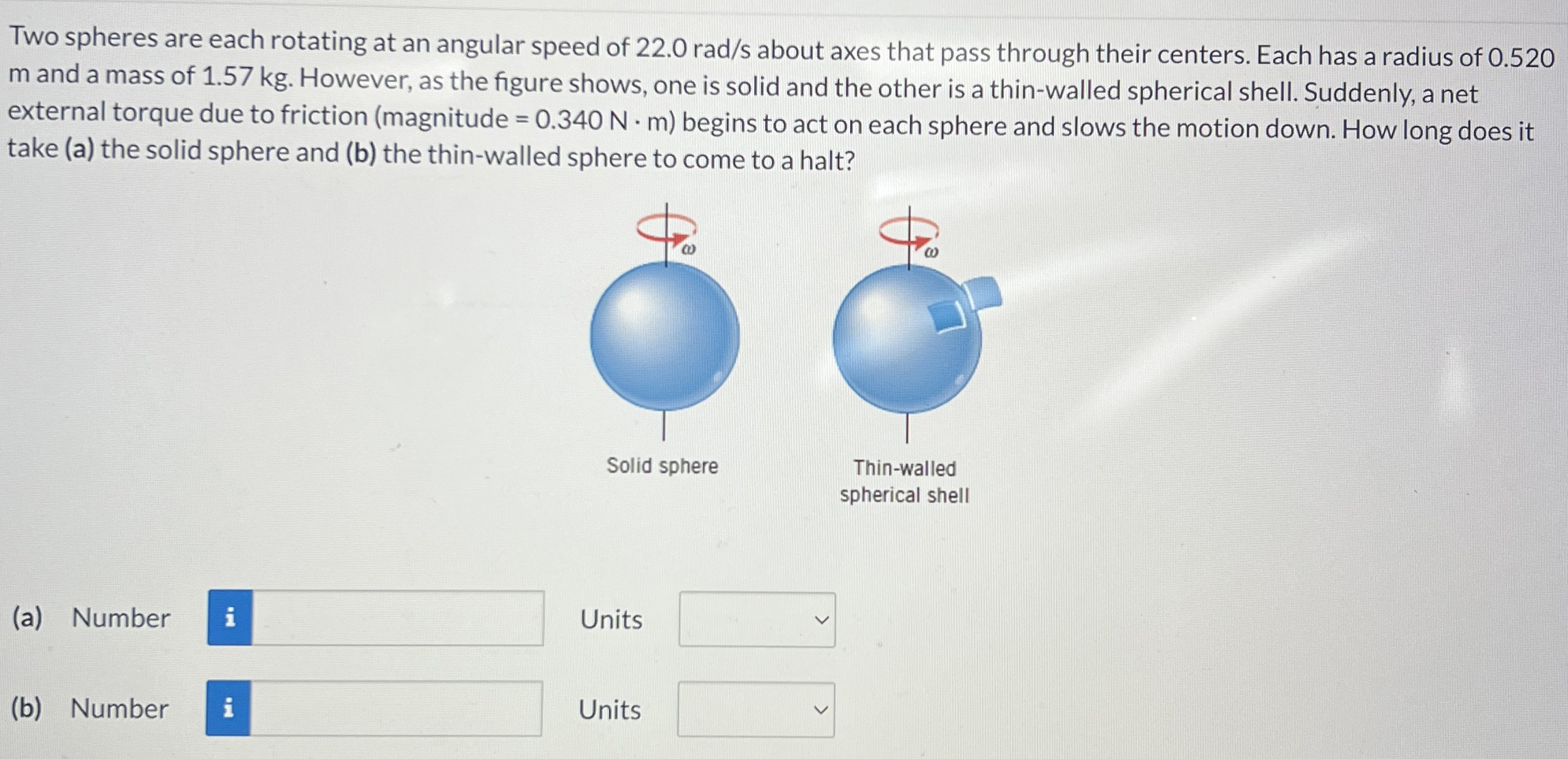
Two spheres are each rotating at an angular speed of 22.0 rad/s about axes that pass through their centers. Each has a radius of 0.520 m and a mass of 1.57 kg. However, as the figure shows, one is solid and the other is a thin-walled spherical shell. Suddenly, a net external torque due to friction (magnitude = 0.340 N⋅m) begins to act on each sphere and slows the motion down. How long does it take (a) the solid sphere and (b) the thin-walled sphere to come to a halt? Solid sphere Thin-walled spherical shell (a) Number Units (b) Number Units